More in Affairs Now
-
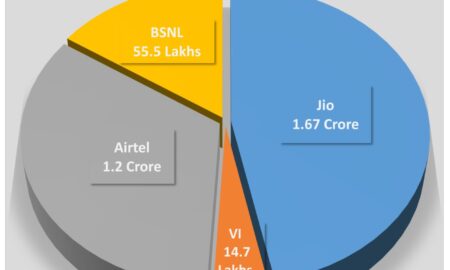
Jio adds 24 times more new mobile subscribers in Odisha
Share the newsJio adds 24 times more new mobile subscribers in Odisha in September than its competitors: TRAI Data Bhubaneswar: Reinforcing...
November 2, 2025 -
UNDP Goodwill Ambassador and ‘Game of Thrones’ star Nikolaj Coster-Waldau highlights Odisha’s mangrove restoration story
Share the newsBhubaneswar, October 22, 2025 – The second season of the acclaimed series ‘An Optimist’s Guide to the Planet’, hosted...
October 23, 2025 -
When Fans Become Victims : Karur Tragedy
Share the newsThe stampede at actor turned politician Vijay’s rally in Karur, Tamil Nadu, on September 27, 2025, has left the...
September 29, 2025 -
Heritage vs. Sanctity: The Controversy Over ASI’s Jagannath Temple Images
Share the newsOn July 29, 2025, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), through its official social media account, posted high-resolution images...
July 30, 2025 -
Celebrating Every Gentle Touch — Himalaya BabyCare Unveils #GentleAsDad Campaign
Share the newsBhubaneswar : Himalaya BabyCare, India’s No.1 Doctor Prescribed baby care brand, unveils a heartwarming DVC film to mark the...
June 15, 2025 -
UDDIPAAN: A Neighbourhood Public Space Reimagined by Adolescents
Share the newsBhubaneswar : Humara Bachpan Trust (HBT), in collaboration with WRI India and Bhubaneswar Municipal Corporation (BMC), proudly announces the...
June 14, 2025 -
Free 2 tractor sand to beneficiaries by Govt to build houses !
Share the newsPradhan Mantri Awas Yojana beneficiaries will get sand for free. The government will provide two tractors of sand for...
June 7, 2025 -
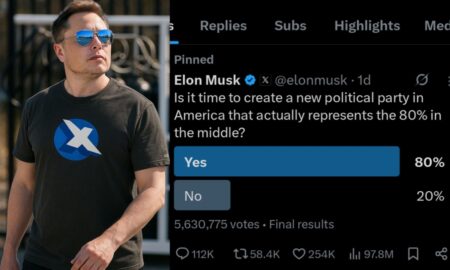
Elon Musk is interested for a new political party in US !
Share the newsThe strong relationship between Elon Musk and Donald Trump has suddenly become strained. Musk previously attended Donald Trump’s cabinet...
June 7, 2025 -
World’s highest Chenab Railway Bridge inaugurated by PM Modi
Share the newsPrime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Chenab Bridge. This railway bridge is the world’s highest arch-shaped railway bridge. Chenab...
June 6, 2025